pectus excavatum baby breathing
HELP DOCTOR THOMAS SURVIVE THE MEDICAL BOARD TRYING TO TAKE HIS LICENSE BY DONATING TO THE CHANNEL. The historical perspective.
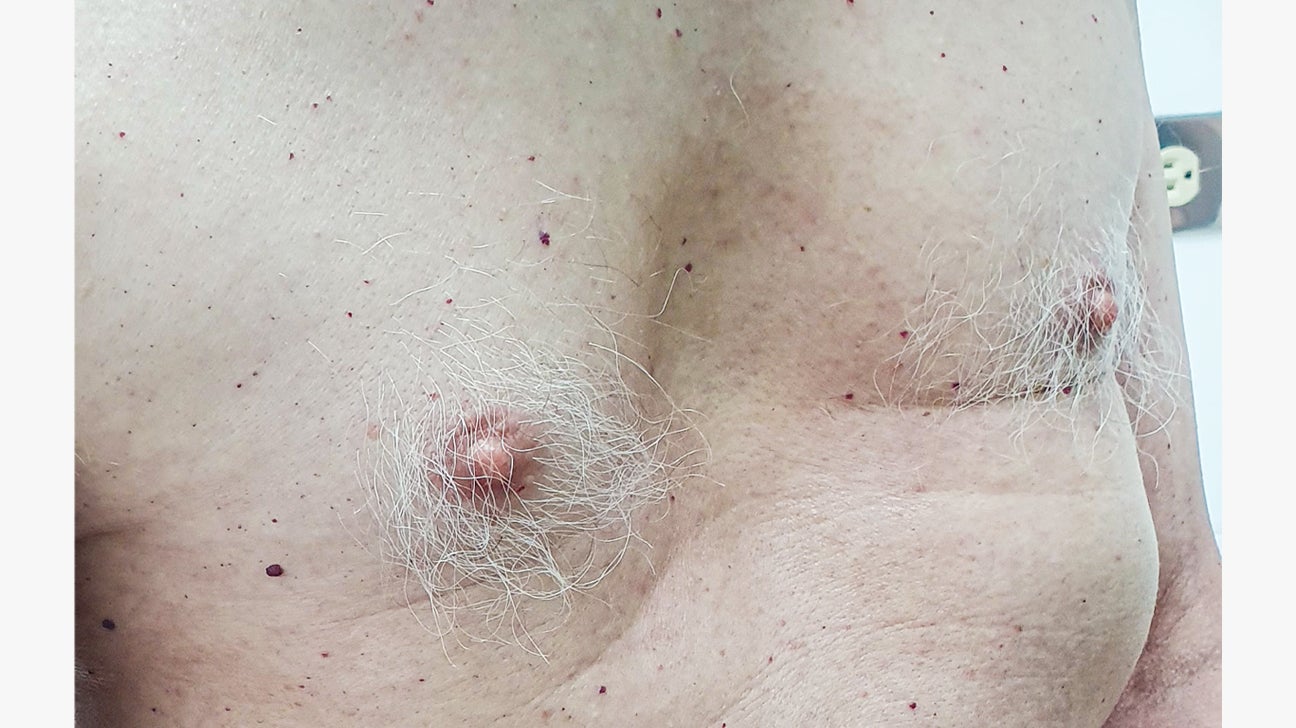
Pectus Excavatum Symptoms Treatments And Complications
Pectus excavatum - dip in babys chest.

. Pectus excavatum may be mild moderate or severe. As the ribcage is more rigid than normal it can make it difficult to completely breathe out expire. The primary goal of surgery for pectus excavatum is to correct the chest deformity to improve a patients breathing and cardiac function.
Also known as funnel chest pectus excavatum is most commonly an isolated congenital abnormality that results in no functional impairment. The next photo shows how the appearance changes with inspiration while crying. The week before volleyball season of my sophomore year I ran 13 timed miles before I finally conquered those long four laps with a time of 857 Miami recalled.
The deformity may be symmetrical the same on both sides or may be more prominent on one side of the chest. If the condition is severe the heart and lungs can be affected. Pectus excavatum occurs in a baby who is developing in the womb.
When the infant is at rest a small depression can be seen over the sternal area. The first recorded description of pectus excavatum was in a 7 years old boy from Spain. The condition affects more boys than girls.
The condition can be mild or severe. It occurs mostly in boys and frequently more members in a family are affected. In older children symptoms of pectus excavatum can include.
Ribcage problems do not usually cause problems when the heart and lungs are developing but rarely can affect how well they work in later childhood. First stretch out the balloon so it becomes more flexible. Take a full breath and exhale in the balloon until your lungs are empty.
Rarely they also have Marfan syndrome. The crying is closely related to chest bone pain which is one of the most common signs of pectus excavatum. This can cause shortness of breath with exercise.
This causes the sternum to grow inward. The opposite condition called pectus carinatum is when the chest bows outward. The condition can be mild or severe.
1 2 Pectus excavatum may be associated with connective tissue disorders such as Marfan and. The lower half of the breastbone may press on the heart and lungs. Some children with funnel chest will live a normal life.
Pectus Excavatum PE is the most common congenital chest-wall deformity in children. Having looked online I see that it can become more pronounced as baby grows and some. It can also develop in a baby after birth.
Then breathe normally and take a second. Pectus excavatum PECK-tuss ex-kuh-VAW-tum is a condition that causes a childs chest to look sunken or caved in It happens because of a defect in the tough connective tissue cartilage that holds the bony part of the ribs to the breastbone. Pectus excavatum is a congenital chest wall deformity that is caused by growth abnormality of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone sternum.
Pectus excavatum funnel chest is when your childs breastbone is pressed inwards and they have a dip between their ribs. Also known as sunken chest or funnel chest pectus excavatum can be corrected with the minimally invasive surgical technique called the Nuss. Pectus excavatum - dip in babys chest.
With pectus excavatum the sternum goes inward to. Pectus excavatum occurs in a baby who is developing in the womb. Pectus excavatum can make breathing a chore but Miami didnt allow her breathing difficulties to stop her from her love for competition.
Pectus excavatum is due to too much growth of the connective tissue that joins the ribs to the breastbone. A community for discussion of Pectus Excavatum. Pectus Excavatum Surgical Repair.
A hollow depression in the chest that may be broad and shallow deep and narrow or irregular. That can be caused by a hard pushing of the breastbone into the lungs. Squeeze the balloon with your fingers so the air wont come out.
More rapid breathing than normal. In 1594 Bauhinus wrote my father showed me a boy 7 years of age among the Nobles of Andalusia who was born with the sternum and ribs being bent back to the internal part of the chest and abdomen so that a large cavity appeared there. For others it may affect their heart or lung function.
It can also develop in a baby after birth. We recently noticed that my little boys chest has a little concave dip in it when he breathes in - the GP has said that he has pectus excavatum and that as his breathing is totally fine it is nothing to worry about. This is typically accomplished by repositioning the breastbone.
Usually the ribs and sternum go outward at the front of the chest. Talk about your personal experiences ask for advice. Pectus excavatum is usually noticeable soon after birth.
Pectus excavatum is a congenital deformity of the chest wall that causes several ribs and the breastbone sternum to grow in an inward direction. This causes a depression of the sternum and the chest has a sunken in or funnel chest appearance. Pectus excavatum is due to too much growth of the connective tissue that joins the ribs to the breastbone sternum.
Children with pectus excavatum sometimes also have scoliosis. In infancy symptoms of pectus excavatum can include. The ideal age for surgical treatment of pectus excavatum is between 12 and 18 years.
The goal of surgery to correct a pectus excavatum defect is to improve breathing posture and cardiac function in addition to giving the chest a normal appearance. Another sign for parents is coughing. This will lower the chances it will blow up in your face.
It is often present at birth but. The symptoms of pectus excavatum depend on when the condition is diagnosed. Studies have shown that pectus excavatum in babies can also cause respiratory infections.
Pectus excavatum is an abnormal development of the rib cage in which the sternum breastbone grows inward resulting in a noticeable and sometimes severe indentation of the chest wall. But this was just normal for me. Pectus excavatum a deformity of the sternum and ribs caused by an unbalanced costochondral hypertrophy is a congenital abnormality with a prevalence of 1 per 1000 patients.
Shortness of breath upon. Make sure youre breathing through the nose and I suggest you look up mewing as it will push your maxilla out of your airway and you will gradually start breathing better and better not referring to the stamina here 2.

Pectus Excavatum Ottawa Citizen
Pectus Excavatum Children S Hospital Of Philadelphia

Pectus Excavatum Chest Wall Stanford Children S Health

Postnatal Photograph Of The Child With Pectus Excavatum Download Scientific Diagram

Pectus Excavatum Background Pathophysiology Epidemiology Pectus Excavatum Medical Pictures Medical
Pectus Excavatum Chest Wall Deformities Child Heart Specialist
Pectus Excavatum Beacon Health System

Pectus Excavatum Symptoms Treatments And Complications

Learning About Pectus Excavatum Repair In Children

Pectus Excavatum Symptoms Treatments And Complications

Low Set Ear Camptodactyly Arachnodactyly Pectus Excavatum Flexion Download Scientific Diagram
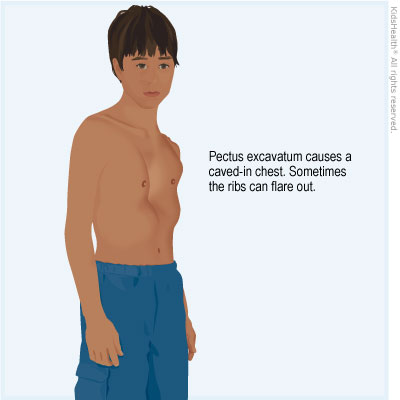
Chest Wall Disorder Pectus Excavatum For Parents Nemours

Find An Ent Doctor Who Knows Laryngomalacia Is More Than Noisy Breathing At Copingwithlm Org Cope Supportive Saving Lives

Help My Baby S Chest Is Caving In Pectus Excavatum Dr Paul Youtube
Should I Worry If My Child S Chest Is Sunken Cincinnati Children S Blog

1 Pectus Excavatum Is Often Seen In Infants This 11 Month Old Child Download Scientific Diagram


/GettyImages-955109626-4b3292cc1af6404d8e85bd1145bd1193.jpg)